Can Birds Eat Meat?
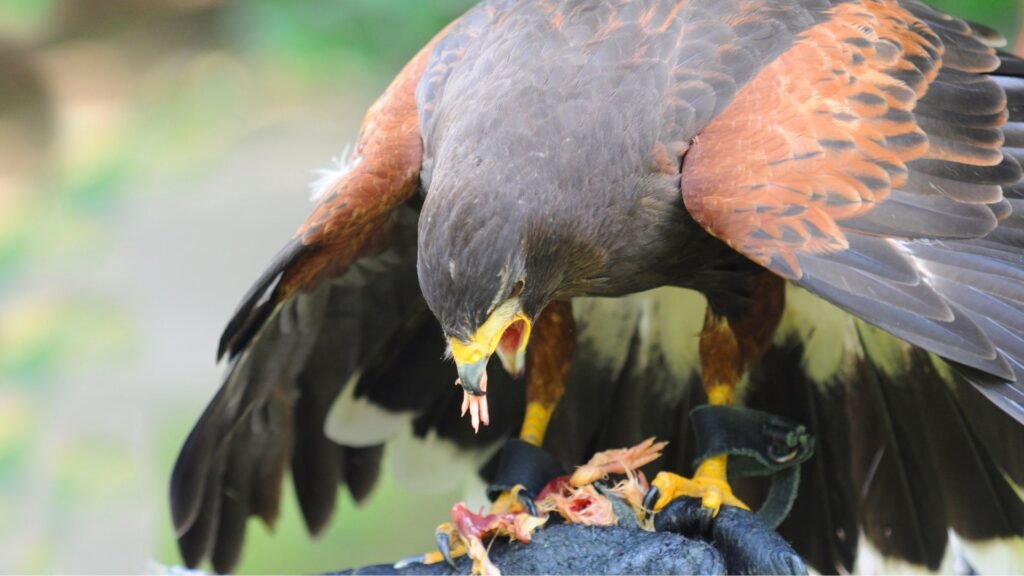

Have you ever wondered if birds can eat meat? What types of birds can consume meat, and what kinds of meat are safe for them?
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of avian diets and behaviors, discussing some examples of meat-eating birds, such as eagles, falcons, and owls. We will explore the reasons why some birds eat meat, the potential benefits and risks of feeding them meat, and how to safely provide meat to birds.
So, Can Birds Eat Meat?
“Birds can indeed eat meat as part of their diet”, with some species being carnivorous while others are omnivorous, showcasing a diverse range of dietary preferences within avian species.
These meat-eating birds have evolved specialized digestive systems to efficiently process and extract nutrients from their protein-rich diet. Raptors, such as eagles and hawks, are known for their sharp beaks and talons, enabling them to catch and consume prey like rodents and fish.
Similarly, owls are nocturnal hunters that rely on their excellent night vision and silent flight to capture small mammals and insects. These avian predators exhibit remarkable hunting and feeding behaviors, perfectly adapted to thrive on a diet consisting primarily of meat.
Types of Birds That Can Eat Meat
Predatory birds, scavengers, and other meat-eating avian species are known to include meat in their diets as a primary food source, showcasing the diverse avian biology and feeding ecology within the avian world.
These birds have developed unique biological adaptations to efficiently consume meat, such as sharp talons for grasping prey, powerful beaks for tearing flesh, and keen eyesight for spotting potential meals from great distances.
Raptors like eagles and hawks are known for their exceptional hunting skills, using their aerial prowess to swoop down on unsuspecting prey. Scavengers like vultures play a crucial role in ecosystems by cleaning up carcasses and recycling nutrients.
Meat-eating birds exhibit a fascinating array of behaviors and physical characteristics that make them formidable predators in their respective habitats.
What Types of Meat Can Birds Eat?
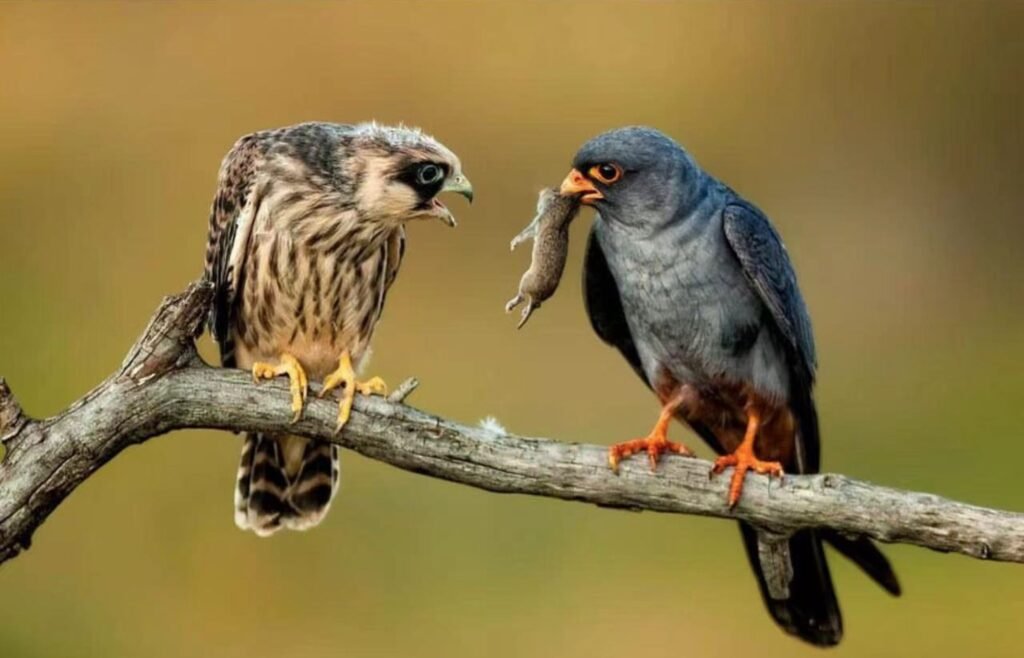

\Birds can consume a variety of meats including prey animals such as rodents, insects, and fish, showcasing their beak and feather adaptations that aid in capturing and consuming meat efficiently.
These adaptations play a crucial role in their survival and ability to secure food in the wild. Birds of prey, for example, have sharp, hooked beaks that allow them to tear into flesh, while waterfowl like ducks have broad bills to scoop up aquatic prey. The sharp talons on their feet are essential tools for grasping and holding onto their catch. Feathers, which are essential for flight, also play a role in protecting the birds during their hunting activities, providing insulation and streamlining their movements for swift, precise attacks.
You might also like: Can Birds Taste?
Why Do Some Birds Eat Meat?
Some birds choose to eat meat due to their specific dietary requirements and nutritional needs, a behavior influenced by their evolutionary history and natural food habits.
For meat-eating birds, consuming animal proteins provides essential nutrients like amino acids, vitamins (such as B12), and minerals crucial for their growth, development, and overall health. These birds often have adaptive physiological traits, such as efficient digestion processes and specialized beaks or talons for hunting and tearing meat. Meat offers concentrated energy sources that enable these bird species to sustain their high metabolic rates, especially crucial during breeding seasons or migratory journeys. Animal behavior plays a significant role in shaping their feeding habits, as instinctual hunting behaviors are vital for survival and reproduction in the wild.
Is Eating Meat Beneficial for Birds?
The consumption of meat can be highly beneficial for certain bird species, providing essential proteins and nutrients that support their evolutionary journey toward optimal health and survival.
In the wild, birds have developed specialized dietary requirements to adapt to their surrounding environments, often relying on protein-rich diets to meet their energy needs and sustain various physiological processes.
By incorporating meat into their diets, birds can efficiently obtain essential amino acids that are crucial for muscle development, feather formation, and overall growth. This aligns with the evolutionary strategies of many bird species, as meat consumption has been a part of their natural diet for centuries, enabling them to thrive in diverse habitats and ecosystems.
Risks of Feeding Birds Meat
While feeding birds meat can offer nutritional benefits, there are potential risks associated with this dietary choice, including the possibility of health problems and environmental impacts on bird populations.
Birds, although they may consume meat in the wild occasionally, have specific digestive systems tailored for a predominantly herbivorous diet. Introducing large amounts of meat into their diets can lead to digestive issues such as bacterial infections, organ damage, and nutrient imbalances.
The environmental consequences of feeding birds meat include unsustainable practices of meat production, deforestation for grazing lands, and increased carbon emissions. These factors contribute to overall ecosystem degradation and loss of biodiversity, impacting not just the birds but the entire ecosystem.
Possible Health Problems from Eating Meat
Birds consuming meat may face health problems related to their feeding habits and digestion processes, underscoring the importance of monitoring their meat intake to prevent potential health issues.
Certain bird species, such as raptors and scavenger birds, have adapted to a diet consisting primarily of meat. While meat provides essential nutrients like protein, iron, and B vitamins, excessive consumption can lead to digestive challenges like impaction and metabolic disorders.
For instance, feeding birds high-fat meats can result in obesity and cardiovascular issues. It is crucial for bird owners and wildlife caregivers to balance their avian companions’ diets with a variety of foods to ensure optimal health and prevent the onset of potential health risks.
Can Feeding Birds Meat Attract Predators?
Feeding birds meat can inadvertently attract predators due to the scent and presence of meat scraps, posing a potential risk to the safety of birds and disrupting the natural wildlife balance.
Such actions can create a chain reaction in the ecosystem, where the increased presence of predators in bird feeding areas can lead to a decrease in the avian population. This shift in dynamics not only affects the bird species directly but also ripples through the entire local wildlife community.
It’s crucial to understand that the act of feeding birds meat, although well-intentioned, can have far-reaching consequences on the delicate balance of nature. Awareness of these implications can help in making informed decisions to protect both birds and the broader ecosystem.
How to Safely Feed Birds Meat?
To safely feed birds meat, it is essential to take specific precautions that accommodate their dietary preferences and feeding habits, ensuring a balanced and safe approach to meat inclusion in their diets.
When introducing meat to birds, it is crucial to consider their natural dietary requirements and feeding behaviors. Birds have different preferences and digestive capabilities, so it’s important to start with small portions of lean, easily digestible meat. Avoid offering processed or seasoned meats as they may contain harmful additives. Monitor their reaction to the new food closely, ensuring that it does not disrupt their regular feeding routine. Gradually incorporate meat into their diet to prevent any digestive issues or health complications.
Safety Precautions When Feeding Birds Meat
When feeding birds meat, it is crucial to take precautions such as ensuring proper storage, avoiding cross-contamination, and adhering to feeding schedules to promote bird conservation efforts and support their nutritional needs.
Safe storage practices involve storing the meat in sealed containers to prevent exposure to contaminants and maintaining a consistent temperature to avoid spoilage. It’s also important to keep feeding areas clean and sanitize them regularly to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria that could harm the birds. Adhering to a feeding schedule ensures that birds receive the necessary nutrients at the right times, promoting their health and well-being. These precautions not only help in conserving bird populations but also contribute to the sustainability of their dietary requirements, ensuring a balanced ecosystem.
How Much Meat Should Be Given to Birds?
Determining the appropriate amount of meat to feed birds involves understanding their feeding frequency, dietary requirements, and ensuring a balance that supports their survival and overall well-being.
Birds’ dietary needs vary significantly depending on their species and natural behaviors. For instance, carnivorous birds like hawks and falcons require a higher proportion of meat in their diet compared to seed-eating birds. It is crucial to consider the nutritional value of meat for birds, as it provides essential proteins and fats necessary for their health. Excessive meat consumption can disrupt the balance of their diet and lead to health issues.
By carefully managing the quantity of meat offered to birds and supplementing it with other foods such as fruits and vegetables, bird enthusiasts can promote a well-rounded diet that supports the birds’ long-term survival.
Best Alternatives to Feeding Birds Meat
Exploring alternatives to feeding birds meat can involve offering plant-based foods, seeds, or specialized bird feed that cater to their dietary needs while providing opportunities for birdwatching and observing natural feeding behaviors.
- By incorporating plant-based options such as fruits, vegetables, and grains into bird feeders, enthusiasts can attract a variety of bird species to their gardens or outdoor spaces.
- Seeds like sunflower, millet, and nyjer are also popular choices as they mimic birds’ natural foraging habits.
- Commercially available bird feed mixes formulated with essential nutrients can help sustain the overall health and well-being of the feathered visitors while allowing observers to appreciate their intricate feeding rituals up close.
You might also like: Do Birds Have Feelings?
Examples of Meat-Eating Birds
Meat-eating birds encompass a diverse group of species, with notable examples including eagles, falcons, and owls that exhibit specialized hunting techniques and avian foraging strategies to capture and consume meat efficiently.
- Eagles, for instance, are renowned for their sharp talons and excellent eyesight, enabling them to spot prey from great distances before swooping down with precision to catch it.
- Falcons, on the other hand, are famous for their incredible speed and agility, which they use to pursue flying birds or swiftly dive to ambush ground-dwelling prey.
- Owls have evolved silent flight and keen hearing to detect small mammals in darkness, making them expert stealth predators in hunting rodents and insects.
Eagles
Eagles are renowned meat-eating birds known for their exceptional hunting prowess and efficient bird feeding behavior, illustrating their role as apex predators in various ecosystems.
They exhibit remarkable aerial skills, utilizing their keen eyesight to spot prey from great distances before swooping down with incredible speed and precision. Eagles primarily hunt by soaring high above their territory, patiently scanning the landscape for potential meals. Once they’ve locked onto a target, they swiftly dive toward the unsuspecting prey, using their powerful talons to grasp and immobilize it. Their sharp beaks are then employed to tear into the flesh and consume the catch. This predatory behavior not only sustains individual eagles but also plays a crucial role in maintaining the fragile balance of nature.
Falcons
Falcons are agile and swift meat-eating birds that exhibit remarkable avian ecology, showcasing specialized adaptations for aerial hunting and unique bird feeding strategies that set them apart in the avian world.
Their sharp talons and keen eyesight make them expert hunters, allowing them to spot prey from far distances and execute precise, high-speed dives to capture their meals.
Falcons’ beaks are not only powerful for tearing flesh but also have a unique notch that aids in severing the spinal cords of their prey swiftly. These feeding adaptations enable falcons to swiftly disable their avian prey, contributing to their success as apex predators in their ecosystems.
Owls
Owls, as nocturnal meat-eating birds, possess specialized bird feeding mechanisms such as silent flight and acute vision, enabling them to hunt effectively in low light conditions and secure a diverse range of prey for their dietary needs.
Their feathers have evolved to reduce noise during flight, allowing owls to approach their prey stealthily. With exceptional night vision, owls can spot their targets from far distances, giving them a hunting advantage in the darkness. Their sharp talons and beaks are perfectly adapted for capturing and consuming a variety of animals, including rodents, insects, and even fish. These specialized physical features highlight the efficiency and success of owls as top predators in maintaining ecological balance within their habitats.






